
In most of the DSLR/Mirrorless cameras, you can increase/decrease the Aperture by 1/3 Stops. So, between f2.8 and f4.0, we will have two more aperture values f3.2 and f3.5.

In the case of 1/3 stop, we are dividing a stop of light into 3 equal parts.
What is aperture setting on a camera full#
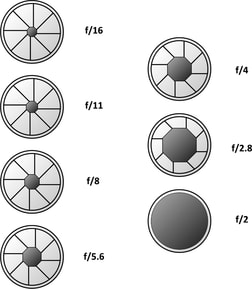
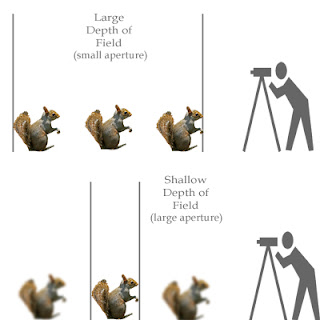
Here, basically, you are dividing one full stop into a half stop. If you go with these values then you will get half of the light that corresponds to next full stop. If you see the ½ stop column in the chart, you can see that there is one aperture value in between each successive full stop. In other words, the light falling in the camera sensor gets reduced by half when you decrease the aperture by one full stop. Here, the f2.8 aperture allows one stop of extra light into the camera when compared to f4. If aperture f2.8 allows x amount of light into the camera, then aperture f4 will allow x/2 amount of light. You can see in the f stop chart that the opening is really big for an aperture value of f2.8 when compared to f11. The term “F stop” can be really confusing if you are a beginner in photography.Ī smaller f-number corresponds to a larger aperture opening and a larger f-number corresponds to a smaller opening. These values correspond to the Aperture value in your camera. You can see three columns- full stop, ½ stop, and 1/3 stop. In this f stop chart infographic, we can see that the Aperture opening is arranged in descending order (w.r.t size of the opening). ApertureĪs you know, the aperture is the opening of the lens through which light enters the camera. We can divide this infographic into 4 sections- Aperture, F stops, Depth of Field, and Exposure. This visual chart will make photography easy for you 😎. The F stop chart infographic is shown above.
What is aperture setting on a camera how to#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
